Project Summary
Exposure to chemical substances that can produce endocrine disrupting effects represents one of the most critical public health threats nowadays. In line with the regulatory framework implemented within the European Union to reduce the levels of endocrine disruptors (EDs) for consumers, new and effective methods for ED testing are needed. The OBERON project will build an integrated testing strategy (ITS) to detect EDs-related metabolic disorders by developing, improving and validating a battery of test systems. It will be based on the concept of an integrated approach for testing and assessment (IATA). OBERON will combine 1) experimental methods (in vitro e.g. on 2D and 3D human-derived cells and tissues, and in vivo i.e. in zebrafish at different stages), 2) high throughput omics technologies, 3) epidemiology and human biomonitoring studies and 4) advanced computational models (in silico and systems biology) on functional endpoints related to metabolism. Such interdisciplinary framework will help at deciphering EDs based on mechanistic understanding of toxicity by providing and making available more effective alternative test methods relevant for human health that are in line with regulatory needs.
Data generated in OBERON will also allow the development of novel Adverse Outcome Pathways (AOPs). The assays will be pre-validated in order to select the test systems that will show acceptable performance in terms of relevance for the second step of the validation process, i.e. the inter-laboratory validation as ring tests. Therefore, the aim of the OBERON project is to support the OECD conceptual framework for testing and assessment of EDs by developing specific assays not covered by the current tests, and to propose an IATA approach for ED-related metabolic disorders detection, which will be submitted to the JRC and OECD community.
CONTEXT
Exposure to chemical substances that can produce endocrine disrupting effects represents one of the most critical public health threats nowadays. In line with the regulatory framework implemented within the European Union to reduce the levels of endocrine disruptors (EDs) for consumers, new and effective methods for ED testing are needed.
KEY OBJECTIVES
The OBERON project aims to establish an integrated testing strategy (ITS) to detect endocrine disruptors-related metabolic disorders by developing, improving and validating a battery of test systems. It will be based on the concept of an integrated approach for testing and assessment (IATA) (figure 1).
OBERON will combine:
1
Experimental methods (in vitro e.g. on 2D and 3D human-derived cells and tissues, and in vivo i.e. in zebrafish at different stages)
2
High throughput omics technologies
3
Epidemiology and human biomonitoring studies
4
Advanced computational models (in silico and systems biology) on functional endpoints related to metabolism
The purpose of such combination is to build a mechanistic understanding of toxicity in order to detect ED. This will help identify effective and alternative tests, relevant for human health and in line with regulatory needs.
Data generated in OBERON will also allow the development of novel Adverse Outcome Pathways (AOPs) and AOP networks.
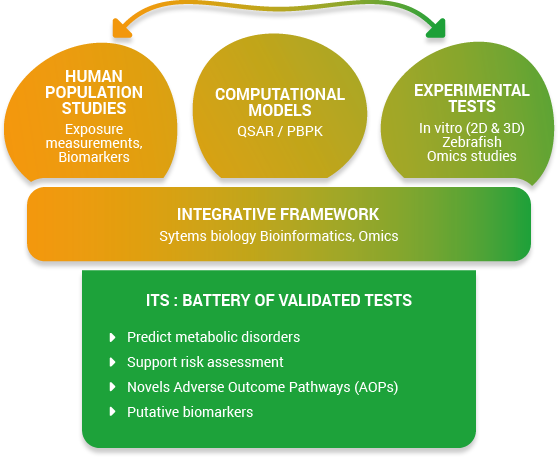
The OBERON platform. Data and model systems that are existing, or that will be developed within the OBERON consortium.
Workpackages
OBERON is organized into eight integrated work packages, specifically designed to foster both transnational collaboration between experts in Europe.
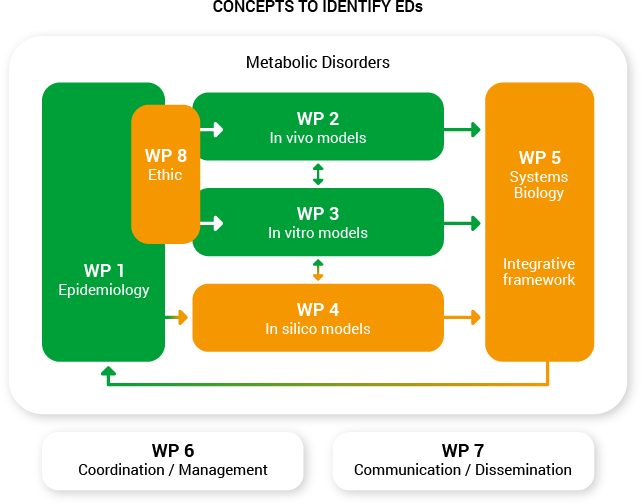
OBERON workplan
WP1 Metabolic health effects of ED exposure in humans
WP1 aims to integrate epidemiology and human biomonitoring studies with the endocrine disruptor test systems for metabolic disorders, in order to increase the relevance of the endocrine disruptor test system. Various time windows will be considered, including developmental periods of high susceptibility (pregnancy-childhood-adolescence) and adulthood. This WP draws on large-scale, population-based study populations including ongoing human biomonitoring studies and some of Europe’s most informative prospective birth cohorts.

Leader

WP2 Disease models using zebrafish
WP2 has for main objectives to set-up, optimize and perform validation of the zebrafish obesogenic test (ZOT) and other zebrafish-based bioassays related to NAFLD, with the aim to screen and identify endocrine disruptors. The identification of potential exposure/pathological omics signatures of obesity and liver pathologies using zebrafish as a model and analytical chemistry analyses data will be provided to produce exploitable data for modeling approaches.

Leader

WP3 2D & 3D models links to organs and tissues
The aim of WP3 is to develop human-relevant test systems to identify ED for metabolic disorders. OBERON will use next generation of cellular toxicity assays by developing innovative technological issues. Different cell systems will be developed from 2D models to 3D cultures which reflect more accurately the organ functionality. Integrative cellular models will be established by developing different co-culture models and extracellular vesicles as potential biomarkers for endocrine disruption will be also implemented. Together with omics profiling, this will support the evaluation of possible EDs effects on metabolic disorders and help establish useful tests for the ITS.
photo credit: Université de Paris - Inserm UMRS 1124
Leader

WP4 QSAR & PBPK modelling
The main objective of this WP is to develop or adapt existing in silico methods for endocrine disruptor compounds. WP4 will develop QSAR and PK/PBPK models in support of the evaluation and integration of the data streams of the project. QSAR can provide pertinent and reliable information about ED potential based on structural information (physicochemical properties of the compounds). Output will be provided to WP5 for integration in hazard and risk decision schemes.
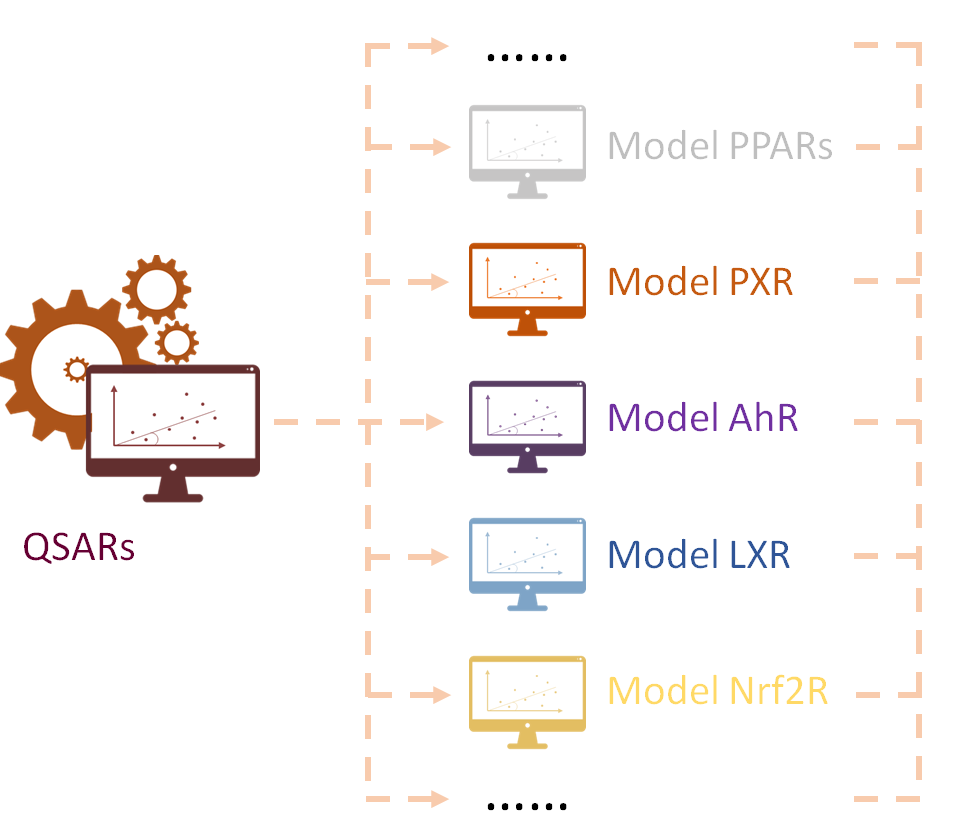
QSAR models
Leader

WP5 Data infrastructure, bioinformatics and ITS
WP5 will use a systems biology pipeline to propose an integrative testing strategy (ITS) for EDs testing.
WP5 aims 1) at integrating existing knowledge and data generated during the project from WP2 (in vivo models), WP3 (in vitro models) and WP4 (in silico models) in order to interpret the WP1 data and make new hypothesis; 2) at providing the tools and computational models for the elucidation of the mechanistic understanding of the links between different levels of biological organization and response, from gene expression to phenotypic response going through proteome and metabolome perturbations related to ED exposure. As a result, existing AOPs will be further advanced and new ones will be developed.

Leader

TRANSVERSAL WORKPACKAGES
WP6 Project management & coordination
The WP6 will ensure the scientific project management, and that the project reaches the defined objectives.
Leader
WP7 Dissemination and exploitation, interaction with regulatory bodies
The main objective of this WP is to organize a well targeted dissemination effort to ensure a maximum impact of the project and release the full exploitation potential of the results.

WP8 Ethics requirements
The objective is to ensure compliance with the ‘ethics requirements’ set out in this work package.


 Download presentation leaflet
Download presentation leaflet